At Maryland Primary Care Physicians, we believe that caring for our patients means caring for the communities they belong to. When one person stays healthy, we all benefit, and when someone is at risk, it’s our responsibility to help protect them.
The Maryland Department of Health has confirmed multiple cases of measles in Maryland. While this may feel like a distant concern to some, we see it differently. As physicians, we understand how quickly this illness can spread, and as members of the community, we know how deeply prevention matters.
This is about more than avoiding an illness, it’s about protecting the people around us. And as we observe National Public Health Week, we want to remind you that public health starts right here. With you. With us. Together.
Why Measles Deserves Our Attention
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, if one person has measles, up to 90% of unvaccinated people who come into close contact will also become infected. The virus spreads through the air and can linger in a room for up to two hours after an infected person has left.
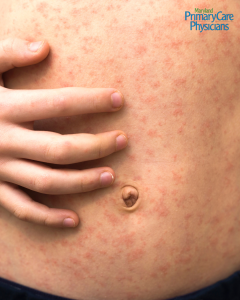 Symptoms usually begin 7 to 14 days after exposure. Early signs include:
Symptoms usually begin 7 to 14 days after exposure. Early signs include:
- High fever (often over 104°F)
- Cough
- Runny nose
- Red, watery eyes
A few days later, a red rash starts on the face and spreads downward across the body.
While most people recover, measles can lead to serious health complications. These include pneumonia, brain swelling, and in some cases, death—especially in young children and those with weakened immune systems. As Johns Hopkins Medicine explains, measles can still be dangerous even with modern medical care. The virus is not gone. It’s just kept in check through vaccination.
Vaccination Is the Best Protection
The MMR vaccine is the most effective way to prevent measles. It is safe, widely available, and incredibly effective.
According to the University of Chicago Medicine, two doses of the MMR vaccine are about 97% effective at preventing measles. The vaccine also protects against mumps and rubella.
Here’s what we recommend:
- Children should receive their first vaccination between 12 and 15 months of age
- A second dose is given between 4 and 6 years old
- Adults who missed one or both doses or who are unsure of their status should speak with a provider
- International travelers and healthcare workers may require additional protection
Vaccination is not just a personal decision. It is a public service. It protects newborns who are too young for vaccines. It shields those going through chemotherapy or living with chronic illness. It helps build a stronger, healthier community for everyone.
Why This Matters to MPCP
Maryland Primary Care Physicians is a doctor-led organization with strong roots in the communities we serve. We are not just here to treat illness. We are here to build relationships, provide trusted information, and help you make decisions that support your health and the well-being of others.
Many of our physicians live in the same communities where they practice. That connection drives our mission. It also informs our approach. We know that public health starts at the local level—in schools, churches, workplaces, and yes, right here in your doctor’s office.
As we recognize National Public Health Week, we want to underscore what this year’s theme—It Starts Here—really means. It means:
- It starts in conversations between you and your provider
- It starts with the decisions you make for your family
- It starts with our shared commitment to care
Let’s Take Action Together
If you need to check your vaccine records or schedule a catch-up dose, we are here for you. Talk to your provider. Book a visit. Encourage your friends and family to do the same.
It all adds up. It all matters.
It starts here.






